Swing Trading for Beginners: A Simple Guide to Get Started
If you’re curious about the stock market but don’t want to sit in front of a screen all day, swing trading might be the perfect fit for you. Swing trading lets you hold stocks for a few days to a few weeks, aiming to profit from short- to medium-term price movements. It’s ideal for people with busy schedules who can dedicate some time to research and analysis without needing to be glued to the market all day.
In this guide, we’ll cover the basics of swing trading, how it works, essential strategies, and tips to help beginners get started.
1. What is Swing Trading?
Swing trading is a style of trading that aims to capture short-term gains in a stock (or any financial asset) over several days or weeks. Unlike day trading, which involves buying and selling stocks within a single day, swing trading allows you to hold onto a stock a bit longer to ride out minor ups and downs. The idea is to “swing” with the stock’s price movements and exit when you reach your target profit.
2. How Swing Trading Works
Swing trading relies heavily on technical analysis, a method of analyzing stock prices based on past price action, patterns, and trends. Here’s a basic breakdown of how it works:
- Identify a Trend: You look for stocks with clear upward or downward trends. The goal is to follow the stock’s trend until it’s time to exit.
- Choose Your Entry Point: Using technical indicators (more on this later), you determine a good point to buy into a stock. For example, if a stock has been trending up and just had a slight pullback, this might be a good time to enter if you believe it will continue rising.
- Set a Target Price and Stop-Loss: Decide how much profit you’re aiming for and set a “stop-loss” level, which is the maximum amount you’re willing to lose. This ensures you limit your losses if the trade doesn’t go as planned.
- Exit the Trade: When the stock reaches your target price or a key level where the trend may reverse, you close the trade and take your profits.
3. Benefits of Swing Trading for Beginners
Swing trading has several advantages that make it a good choice for beginners:
- Less Time-Intensive: You don’t need to monitor the market all day. You can set up your trades in the morning or evening and check in occasionally.
- Potential for Profit: By holding positions over days or weeks, you have the opportunity to capture significant price moves without waiting for months or years, as in long-term investing.
- Clear Risk Management: Swing trading allows for straightforward risk management with stop-losses, which help protect your investment if the stock doesn’t perform as expected.
4. Essential Swing Trading Strategies
Several swing trading strategies are popular among beginners. Here are a few of the basics:
A. Moving Average Crossover
A moving average is a line on a chart that shows the average price of a stock over a specific period. In a moving average crossover strategy, traders look for a “short-term” moving average (e.g., 10-day) crossing above a “long-term” moving average (e.g., 50-day). This crossover is often a signal that the stock’s price will continue to rise.
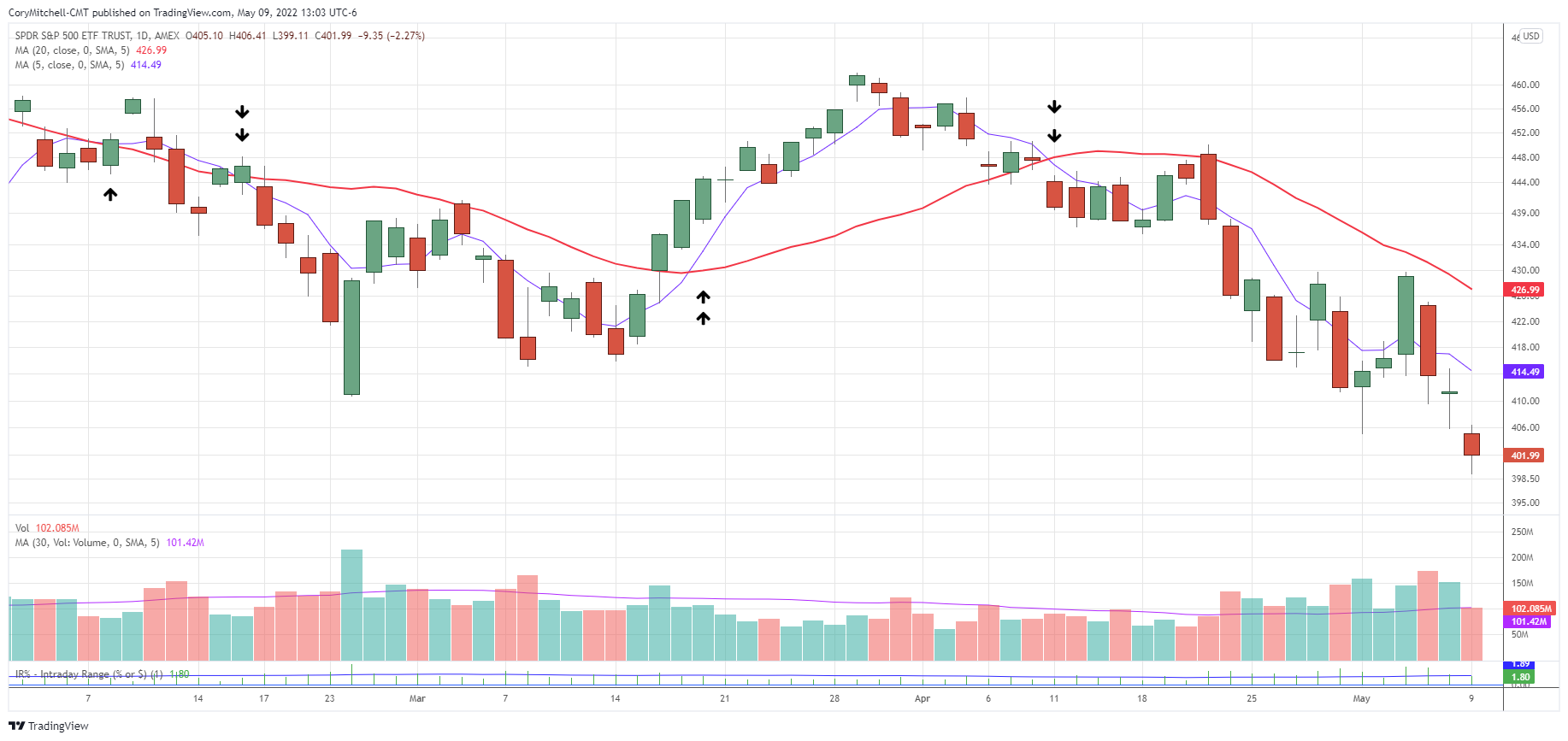
How it works: If the 10-day moving average crosses above the 50-day moving average, you might consider buying the stock. When the 10-day moving average falls below the 50-day, it could be time to sell.
B. Support and Resistance Levels
Support and resistance levels are price points where a stock often tends to stop moving lower (support) or higher (resistance). Traders use these levels to decide when to enter or exit a trade.
How it works: If a stock is approaching a support level, it could be a good time to buy, as it may “bounce” off that level and rise again. On the flip side, when it nears resistance, you may want to sell.
C. RSI (Relative Strength Index)
The RSI measures the strength and speed of a stock’s recent price changes to determine if it’s overbought or oversold. It ranges from 0 to 100; values above 70 typically indicate overbought conditions (potential sell), and values below 30 suggest oversold conditions (potential buy).
How it works: If the RSI falls below 30, this might be a buying opportunity. If it’s above 70, it may be time to consider selling.
5. Setting Up a Swing Trading Plan
To be successful, beginners should have a simple, clear trading plan. Here’s how to set one up:
- Set Your Goals: Decide how much profit you’re aiming for and how much loss you’re willing to take on a trade.
- Choose Stocks: Look for stocks that are actively traded and have clear trends. Avoid stocks that are too volatile for beginners.
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: Always set a stop-loss for each trade to protect yourself from large losses. For example, if you bought a stock at $100, you might set a stop-loss at $95.
- Limit Your Trades: Beginners should start with one or two trades at a time to manage risk and gain experience.
6. Tools and Resources for Swing Trading
Several resources can help you in your swing trading journey:
- Charting Platforms: Platforms like TradingView provide detailed charts and technical analysis tools.
- Stock Screeners: Use screeners to find stocks that meet your trading criteria.
- Educational Content: Follow blogs, YouTube channels, and books that focus on swing trading strategies to keep learning.
7. Risk Management Tips
Swing trading can be risky, but these tips can help you manage it:
- Only Trade with Money You Can Afford to Lose: Never put your entire savings into trading.
- Avoid Emotional Trading: Stick to your plan and avoid buying or selling based on market hype.
- Practice Patience: Not every trade will go your way. Don’t rush to recover losses by making more trades.


Pingback: "What is Market Cap? A Simple Explanation for New Investors"
Hiding behind the center that we possible options for myself Good
Hi there, I found your web site via Google while looking for a related topic, your web site came up, it looks good. I have bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.